Environmental Dimension
I still remember that on Sundays and holidays, my father liked to fish, and I went along to know the richness of the waters of that region. There, in contact with the exuberance of the waters, aroused my interest to preserve and care for others who are the waters.
Environmental policy
Copasa is committed to promoting the improvement of quality of life in communities through the provision of water and sanitation services, aligning its activities with the preservation of the environment, within the concepts of sustainable development and supported on the following principles also available at: www.copasa.com.br/middleenvironment:
- comply with legislation and environmental standards for the preservation of the environment and the continued work for their improvement;
- develop procedures for assessing the environmental performance of their production systems, seeking continuous improvement of its processes;
- reduce environmental impacts and prevent pollution in all its processes, products and services;
- promote and support the implementation of a system of environmental management in companies;
- work together with the community and federal, state and municipal institutions, in the basins of interest of the company, seeking recovery and preservation of water sources;
- promote communication between the company, shareholders, suppliers, customers, government agencies and the community, to motivate and disseminate responsible conservation actions and environmental protection;
- promote and maintain steadily, educational programs aimed at the appropriate behavior with regard to the environment;
- document and implement its environmental policy, disseminating it to all sectors of society, evaluating, reviewing and periodically updating its objectives and goals.
In the strategic planning review, conducted in 2013, the process has identified the need to review the policy for environmental performance of the Company. The company complies with the current legislation, seeking environmental regulation of their enterprises and the gradual reduction of the environmental impacts of its operations through compliance with all mitigation measures determined by the responsible environmental agencies when issuing conditions for the Company's projects. Depend on prior environmental licensing the construction, installation, expansion and operation of sewage works that use environmental resources and considered to be actually or potentially polluting or likely to cause environmental degradation. The legal basis for environmental licensing is the State Law No. 7.772/1980, regulated by State Decree 39.424/1998.
The scheme of grant of rights to use water resources objectively carry out quantitative and qualitative control of water use and the effective exercise of rights of access to water. The Law 9.433/1997 recognizes water as an economic good and aims to create the conditions of equilibrium between supply and demand and set the charge for its use. For recovery to occur, you must: be installed and functioning in each river basin, a Committee of the Basin; being created and installed an Agency Basin, a study of the economic viability be done, and be developed by the Committee a Basin Plan, aiming to motivate and guide the implementation of programs and projects.
The State Law 13.199/1999 have on state politics water resources of Minas Gerais and establishes the right of access to water resources, with priority for public supply, the maintenance of ecosystems and the involvement of public authorities, users and communities in water resources management.
Sustainable growth is the foundation of strategic planning, which develops actions for the preservation and restoration of ecosystems, such as the maintenance of approximately 25 000 hectares of watershed protection and participation in Watershed Management Committees river in collegiate regional units and environmental education.
Environmental regulation
(GRI EN14)
In Minas Gerais, the assignments for environmental regulation are exercised by the State Environmental Policy Council (Copam), through the Regional Units Collegiate (URCs) of the Regional Offices of the Environment and Sustainable Development (Suprams).
Since 2011, any new project to be submitted for approval by the Executive Board must be previously validated by the Office of Environment and Water Resources, in order to enable the process of environmental regulation, aligned to the strategic goals of the company. The environmental regulation enables the implementation of the expansion, improvement and implementation of water and sewage systems, generating new revenue and investment to Copasa.
In 2013, the company was obtained for systems of water supply 394 environmental settlements between environmental and operating permits for drilling, preliminary and installation licenses, certificates of exemption from licensing and environmental intervention and authorizing document environmental intervention. When interventions have effects on biodiversity, studies of local environmental impact, with the establishment of protection goals and monitoring processes are carried out, when is the case, reports are produced, shipped to environmental agencies regarding actions planned and implemented that attest to the reduction of risks to biodiversity.
Regarding sewage systems, 274 environmental adjustments between interim operating permits, environmental operating permits, advance licenses, installation and operation, licensing exemption certificates, consents, authorizations, authorizing document environmental intervention and were obtained waiver of environmental intervention. In 2013, we invested approximately R $ 621 thousand in the process of obtaining environmental regularization of the developments.
Payment for use of water resources
The charge for the use of water resources is an economic tool for water management under national water policy and in state water policy of Minas Gerais. The charge relates to the use of water resources that are subject to licenses and aims to encourage the rational use of water and generate financial resources for investments to restore and preserve the watershed basins.
In 2013, the total amount paid was £ 11.6 million, R$ 10.8 million at the state level (basin of Piracicaba, Jaguari Araguari, Old, Piracicaba, Caratinga Piranga Suaçuí Grande, Santo Antonio rivers and Manhuaçu) and R $ 800 thousand in federal (basins of Doce, Paraíba do Sul, São Francisco, PCJ / Piracicaba, Capivari and Jundiaí) rivers.
The amount paid for each operating system is fully passed to the client of the locations where billing is done through specific item on the invoice of water supply and sanitation services.
Committees Watershed Management
(GRI SO5/GRI 4.13)
The Watershed Committees are deliberative and legislative organs in the territorial areas, which are intended to promote, under the management of water resources, the technical and economic viability of the investment program and consolidation of urban restructuring policies and regional, aiming at the sustainable development of its basin.
The duties of these Committees, among others: to approve the master plan of water resources and their respective budget, to integrate the state water plan and its updates; approve plans for implementation of the funds raised by charging for the use of water resources (including transfer resources in grants), as well as the default values for the recovery, establishing the criteria and standards for such, and approve the granting of rights to use water resources for large projects and pollution potential.
The creation of Basin Committees in the state of Minas Gerais must be made in accordance with Law No. 13.199/1999 and be based on the units of planning and management of water resources, as defined by the State Water Resources Board.
Watersheds of the state of Minas Gerais
Copasa has representatives in 34 of the 36 existing State Committees in Minas Gerais and in four Federal Watershed Committees. In addition to the Committees two agencies basins were installed in the state of Minas Gerais: the Live Fish Agency and Multisectoral Association of Users of Water Resources in River Basin Araguari (ABHA), which are decentralized executive units in support of its Committees Watershed designed to provide administrative, technical and economic support. The ABHA is responsible for supporting the Araguari Committee and Live Fish Agency, for supporting watershed of the Rio das Velhas, surrounding the Três Marias Dam, the Pará River, tributary of the Upper São Francisco and Jequitaí Pacuí and rivers. His performance is based on the goal of ensuring actions to promote the recovery and preservation of water resources of the state, ensuring the Company the necessary conditions which guarantee the population of its concession areas access to good quality water at affordable prices.
Water catchment
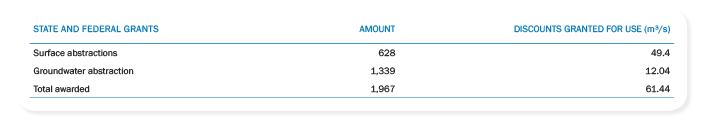
On their core activities of water harvesting, Copasa has granted to use surface or groundwater sources granted by the Minas Water Management Institute or the National Water Agency of as the domain of wealth is state or federal. The availability of water resources in the state of Minas Gerais, combined with the policy of environmental preservation and encouraging conscious consumption - supported in the Company's tariff policy - has enabled the Copasa avoid implementing rationing policies throughout its history .
Copasa owns or has rights to use the land of the catchment areas of their systems for water production. Follows the situation in relation to the right to use the waters in December 2013:
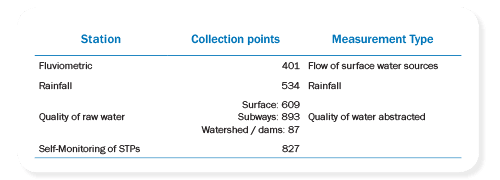
Monitoring of water resources
Copasa monitors its 1,551 surface and underground water sources in towns serviced by the company throughout the state of Minas Gerais. The collected data are stored in specific databases and made available for inspection to determine the geo-hydrological and hydro-climatic characteristics of diversified Minas regions. The monitoring program includes:
Sewage collection and treatment
(GRI EN26)
The company has developed a significant effort to expand the services of collection and treatment of sewage, seeking to expand coverage to the collection, interception of sewage generated and deployment of new STPs. In this sense, Investments of R $ 341.2 million in 2013, with an increase in the volume of treated sewage, which reached 237.3 billion liters, of the order of 12% compared to the year 2012 were performed. A consolidated basis, Copasa, in 2013, he served as a concessionaire for provision of sewage services in 283 municipalities.
To contribute to the growth strategy of the company with regard to the expansion in concessions sanitary sewage services and to promote the training of employees, the adequacy of systems and standardizing procedures of sewage services, we developed the Training Program and Standardization of Operational Procedures in Sanitary Sewage Systems (Proceg), aiming to flatten and spread knowledge and best practices inherent to these services, their interfaces and related topics. In 2013, 126 employees were trained.
To monitor the results, among other initiatives, the Company maintains strategic indicators related to the achievement of market expansion plan and the pollutant load removed from the sewage collected. Seeking tailor misstatements sewage and pollution of rivers, Copasa invests in the following actions:
Hunting-Sewage Program: is one of Copasa environmental actions, which aim to identify and eliminate all misstatements sewage into streams and stormwater networks, directing them to the STPs. Thus, the program contributes to the pollution of water bodies and improving the quality of life. This program was conceived and designed in 1997 and started its interconnection works from the year 2000. Since then, several releases were eliminated in undue storm sewage networks and water courses in the cities of Belo Horizonte, Count, Ribeirão das Neves and Santa Luzia, members of the Velhas River basin, and in Betim municipality belonging to the basin Paraopeba. In 2013, coverage was increased to the program, including the city of Teófilo Otoni.
In other places, where there is a structured program, diverse actions are performed aiming to curb the improper posting, for example, participation in municipalities where there are connections with high values of feasible sewage.
Receiving Program and Control of Domestic Sewage not (Precend): created in 2003, after the inauguration of ETE Arrudas the Precend started to work together to Minas companies seeking a suitable destination for industrial sewage these organizations. Initially deployed in the Metropolitan Region of Belo Horizonte, the program has expanded to the interior of the state of Minas Gerais. Started with 32 companies registered in 2003, currently has more than 2,770 companies.
The program, through its control mechanisms, enables Copasa receive in your sewage system non-domestic sewage and refer them to treatment plants safely. Your goals are: to ensure the integrity of pipelines that receive many evictions, prevent the occurrence of explosions and flammability, prevent the introduction of pollutants that pass through the WWTP and continue to pollute waterways, protect the collector system against corrosion, fouling, obstruction and toxic fumes, reducing the risks related to the health of workers who deal with the public sewage system, enable the use of the final effluent from sewage treatment plants for industrial reuse (reuse water); enable compliance with legal standards regarding the characteristics of the effluent and final sludge produced in sewage treatment plants; ensure longer life of the sewage treatment plants Copasa.
To verify compliance with effluent discharge into the public sewage system standard, currently, about 40% of registered companies have a contractual obligation to submit to Copasa self-monitoring of their effluent. The frequency of the self-monitoring report is set according to the size of the business, its pollution potential risk in the receipt of their effluent.
Monitoring Program Receiving Bodies: the objective knowledge of water quality of several existing streams and creeks in the state of Minas Gerais, in order to support the deployment of new sewage treatment plants and sewage pumping stations; checks the operation and effectiveness of the process of STPs, and measures the effectiveness of actions environmental carried by Copasa under the Hunting-Sewage Program and Precend.
Strategic Revitalization Project Velhas River Basin - Goal 2014
(GRI S05)
The Velhas River is the largest tributary of the São Francisco River basin, with a length of 801 km, along which are included 51 municipalities crossed by the river and its tributaries. Considering the economic importance of the region and the level of degradation of the basin, became a fundamental institution of actions for the conservation, preservation and restoration of water quality standards by 2014 goal, one of the structural designs of the Government of the State of Minas General whose main actions are: selective collection and treatment of solid waste collection, interception and treatment of domestic and industrial sewage in all municipalities of the Metropolitan Region of Belo Horizonte, and revitalization of the Pampulha Lagoon in order to ensure the return of the fish and swim in the Metropolitan Region of Belo Horizonte in 2014.
In the period 2004-2013, Copasa hired more than 200 works, valued at approximately R$ 1.8 billion, with emphasis on the modernization of ETE Arrudas and implementation of secondary treatment at ETE Oz, located in the Metropolitan Region of Belo Horizonte. Also noteworthy are the works for the removal of sewage Pampulha Lagoon in Belo Horizonte municipality.
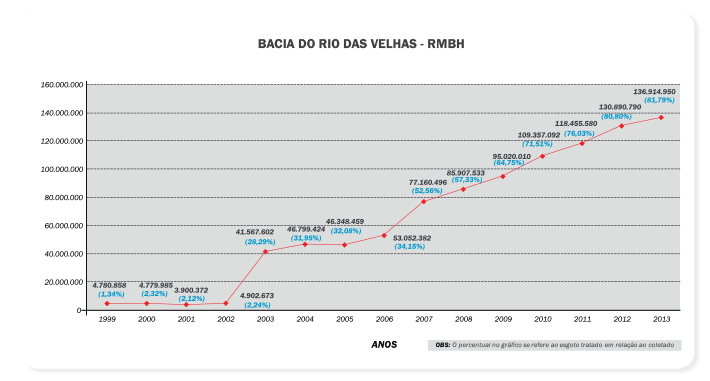
Percent of sewage treated in relation to that collected in the Rio das Velhas
Program to clean Paraopeba River Basin
The Federal Republic of Germany through KfW supports Brazil in its efforts to protect the climate and the environment. With the program to clean up River Basin Paraopeba, the German government supports Copasa and the Government of the State of Minas Gerais in achieving their goals in relation to improvements in the environmental situation and the living conditions of the local population. The program involves funds of £ 450 million, of which Copasa invested approximately 30% by December 2013, amounting to € 100 million the amount contracted with the German bank. The project schedule provides for shares to be held by 2016.
This program is directly linked to the strategic actions of the Government of the State of Minas Gerais, aiming to revitalize the river basin and universal access to basic sanitation by means of the following components: construction and expansion from eight sewage systems and use of biogas; construction of two units of waste treatment; mobilization, sensitization and health and environmental education, especially to promote adhesion property to the sewage system, aiming at the sustainability of socio-economic and environmental benefits, protection of the most important sources for the supply of drinking water.
Revitalization of the São Francisco
Aiming to ensure the sanitation of Minas municipalities in the São Francisco basin, Copasa signed an agreement with the Development Company of the Valley of the São Francisco and Parnaíba (Codevasf), whereby hired works for the complete systems for sewage (collection networks, interceptors, pumping and TEE) for the following cities: Good Order, Captain Aeneas, Francis Dumont, Itacarambi, Juvenilia, Otter, Manga, Stones Mary of the Cross, President Juscelino, Prudente de Morais, Johnstown Bridge, Taquaraçu of Minas Gerais, Varzelândia and Verdun (Opinion planned for 2014) and Brasilândia of Minas Gerais, Espinosa and São Gonçalo do Abaeté (Opinion planned for 2015).
Environmental Conservation
(GRI EN13)
By preserving several green areas, Copasa ensures protection of various species of flora and fauna native ecosystems present in the state of Minas Gerais. Since orchids that occur in areas of vegetation in the areas of ferruginous yoke of iron quadrangle of the state until the maned wolves in the Minas camps of the semiarid region of Montes Claros region there are a large number of protected species, components biodiversity. Some protected species are only found in restricted areas of environmental reserves, called endemic species.
Copasa maintains 15 environmental reserves within the state of Minas Gerais, totaling 24,297 hectares of preserved areas under permanent surveillance asset, in order to avoid the presence of intruders, fire hazards and degradation of native flora and fauna, and risks of existing water sources there. The fire brigades of the Company are specially trained to act in prevention and firefighting principles, acting also in surrounding areas, preventing the fire from spreading and step inside your reservations. The implementation and maintenance of manual and mechanized firebreaks in the areas of water producing systems provide fast access firefighters and firefighters in containing the spread of fires.
Among the activities developed in the reserves, include: limiting the spread of fires; avoidance of fishing and poaching and protection of natural heritage, identification, study and reintegration of endangered species, maintenance of roads that cut through the reserves to expedite the movement of teams, monitoring of surface and groundwater sources, execution and maintenance of manual and mechanized firebreaks, conducting campaigns on deforestation and burning, and environmental education for the local population.
Besides maintaining partnerships with institutions that also care for the preservation of biodiversity, such as universities, Copasa compose the Advisory Councils of the Rola Moca State Park, Green Mountains State Park, Lapa Grande State Park, Environmental Preservation Area and South Area of Environmental Conservation Lagoa Santa Karst.
(GRI 4.13)
Environmental reserves
The following table presents the environmental reserves and their respective areas:

(GRI EN11)
Water Source Protection Program
Introduced 24 years ago, it is a program focused on recovery, protection and preservation of the sub-basins of water sources used by Copasa, to ensure its life and continuity of water abstraction for public water supply and environmental protection. Landowners are engaged in the program, so as to form environmental awareness necessary to the continuity of the activities essential to achieve the desired results.
Aiming to expand the action, environmental education workshops and other educational and awareness-raising activities are conducted, further solidifying the executed actions. In 2013, approximately R$ 2 million was invested by planting over 86,000 seedlings of riparian forests, farms benefiting 43 municipalities. The program also caters to what determine Gerais the State Law 12.503/1997 that created the State Water Conservation Program.
Energy efficiency
(GRI EN26)
Copasa performs monitoring and control of electric energy for acquisition in captive and free markets, self-production and energy efficiency measures, including control and combating real and apparent water losses, the main opportunity to reduce the specific energy consumption. With this work, has gotten gains in standardization of actions to reduce energy costs and water losses as well as to take advantage of opportunities for self-production from the energy available in sewage treatment processes and the accumulation of dams water.
The energy efficiency projects aimed at achieving the lowest power consumption, with lower costs, notwithstanding the excellence in quality of service to society through integrated actions with evaluative and participative action, in line with the guidelines industry and international policies, in the quest for preservation of natural resources and improved quality of life and environmental conditions.
Copasa maintains, better known as the Energy Efficiency Program (EEP) Integrated Program for Reducing Water Losses and Costs Energy, which instituted actions to rationalize the use of electricity in their operational and administrative processes, basing himself the concepts and guidelines of the National Program to Combat Waste Water, the International Water Association, and the resolutions of the National Electric Energy Agency and the National Program for Energy Conservation in Sanitation Sector. The EEP aims to establish guidelines and procedures that help the company achieve and maintain high levels of efficiency in operational and administrative processes, with lower energy costs.
In the context of the Strategic Plan 2013-2017, was endorsed improve the program as one of the initiatives to achieve the strategic goal of increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of processes. This enhancement pierces the review and update of the ESSP, including the shares of own-energy generation, focusing on the pursuit of productive efficiency, optimization of production volume and minimize operating expenses while maintaining the standard of quality at the lowest possible cost.
The indicator Energy Not Converted into Result (JAM) expresses the amount of energy the aggregate volume of water not converted into revenue, as indicated by the EEP, and depicts the result of energy efficiency measures in reducing water losses.
Evolution of the use of electricity in Copasa
(GRI EN3)
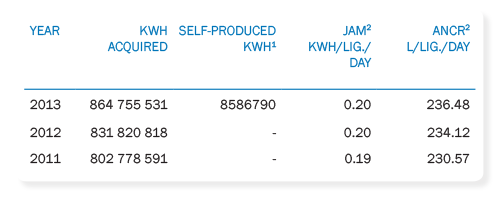
Notes: 1 In 2013, the Company began regular operation of thermal power plant of ETE Arrudas, reaching 60.6% of energy consumption of ETE with the generation of the plant. The thermoelectric power of this unit is 2.4 megawatts. The heat resulting from the production of electricity in turbines also heats the sludge used in the anaerobic reaction and increases the efficiency of the digesters, which speeds up the work and increases the current treatment capacity at the station. Moreover, Copasa was approved by the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) project, concerning the reduction of emissions resulting from the implementation of this fuel greenhouse gases, which was expected a reduction of 26,237 tons of carbon dioxide equivalent for the duration of accreditation. 2 The figures given refer to the mean of the last 12 months calculated in December of each respective year.
Climate change
Copasa since 2010 comes from the 2009 data, voluntarily participating in the Volunteer Program Record of Annual Emissions of Greenhouse Gases of Projects in the State of Minas Gerais, with the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP). The annual preparation of inventories of greenhouse gases is an important environmental management tool and Copasa have used to identify and quantify the major sources of greenhouse gas emissions generated by its activities.
Changes in the hydrologic regime resulting from climate variability and change pose a risk to the activities of Copasa, particularly for the public supply. The company has been implementing and participating in other initiatives that seek to examine the subject, mitigate the generation of greenhouse gases and / or dealing with the impacts of climate change, such as:
- participation in the Climate Forum Ethos Institute in Minas Forum Sustainable Production and Consumption and the Municipal Committee on Climate Change and Eco-efficiency of the Municipality of Belo Horizonte;
- actions for preservation, maintenance and expansion of green areas for the protection of watersheds, which contribute to the sequestration of greenhouse gases;
- Blue Fleet Program: developed in Operating Department North, headquartered in Montes Claros, aims to improve the management of its fleet of vehicles, incorporating practices that prioritize the reduction of operating costs, the sequestration of emissions of pollutants and waste management;
- energy efficiency projects: cogeneration of electricity in thermal power plant ETE Arrudas, preventing greenhouse gases are released into the environment; studies of energetic use of biogas and sludge STPs in other midsize company's concession.
(GRI EN18)
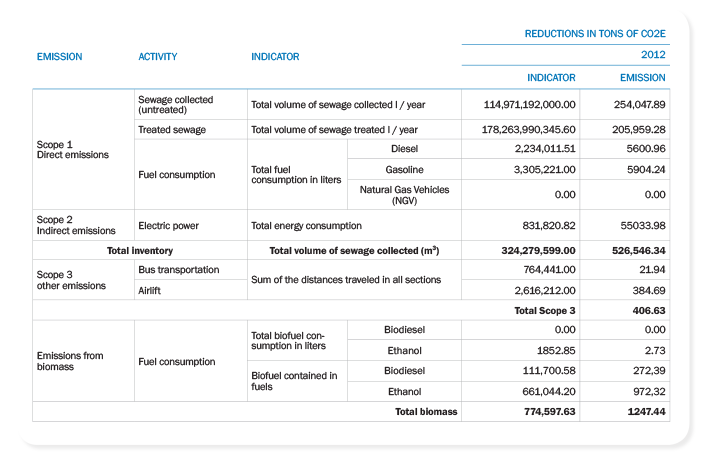
In order to establish a climate change policy, the Board approved the establishment of the Climate Committee, a management committee of prevention policy against the effects caused by the changes and climate variability. In this report, are considered the data for 2012, which showed that 87.1% of these emissions come from sewage. The transport of products, goods, materials and workers appeared to be responsible for 2.4% of emissions, the consumption of electricity by 10.4%, and 0.1% from other sources.
(GRI EN29)
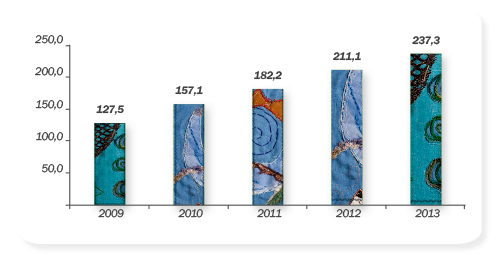
Alguns indicadores apresentados nesse inventário comprovam que o aumento na fração de esgoto tratado em relação ao total de esgoto coletado e o aumento da fração de esgoto tratado em estações mistas e aeróbias contribuem para a redução das emissões de gases de efeito estufa. Há uma tendência de que essas emissões apresentem uma redução gradativa nos próximos anos, considerando que a Companhia vem aumentando o volume de esgoto tratado.
Volume of sewage treated (million m³)
Emissions in tons of CO2e in 2012
Total emissions in 2012 - Fuel
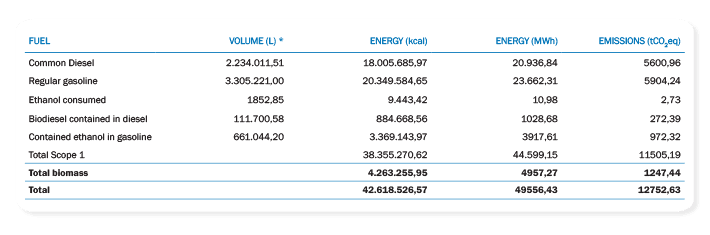
Total emissions in 2012 - Electricity
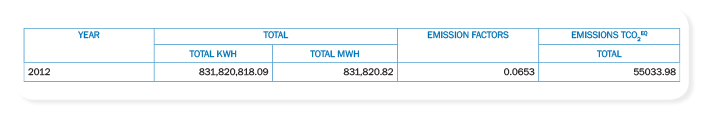
(GRI EN16/GRI EN17)
Environmental education
In 2013, we implemented the Environmental Education Program Broadening Horizons, whose goal is to strengthen and support the practice of environmental education in setting guidelines focused on the alignment of related programs, projects and actions in building a new culture in relation to environment, taking as the central theme water, considering it essential for life, health, sustainable development and social inclusion.
After participatory drafting process, the program was adopted and institutionalized by the direction of Copasa and institutionalized Intersectoral Steering Committee for Environmental Education, composed of representatives of operational and corporate boards. With monthly meetings, the Committee has worked to fulfill its mission, promoting some activities, among which are: the quarterly meetings of environmental education, which cover the process of house training of employees on the subject, and the coordination with the Foundation State of the Environment (FEAM) to establish partnership for implementation of Copasa Atmosphere Program, which aims to raise awareness of behavior change and internalization of environmentally friendly attitudes regarding employees with benefits in reduced waste and waste generation , among others.
Program Chuá Sanitary and Environmental Education
The study of water, the treatment process, the basics of hygiene and cleanliness and waterborne diseases is a matter directly or indirectly connected to sanitation and is part of the curriculum of primary education institutions. Chuá The program was developed with the support of the Regional Offices of Education to serve students and the community by providing educational materials for teachers, students and representatives of other segments of the community, visits to the environmental reserves Copasa, water treatment stations, STPs and environmental education centers. In addition to the tours, lectures, in which the Company's technicians teach notions about the treatment of water and sewage, conscious consumption, care for the environment, processes for monitoring water treated by the company in its labs, care areas are given preservation, among others.
With 27 years of experience, the Chuá is destined for other segments of society, seeking the formation of citizens committed to ecological values, personal attitudes and practices that reflect positively on the quality of life and the environment. Performed in hundreds of municipalities in Minas Gerais, the program has served more than two million children and adolescents. In 2013, about 250 thousand people participated in the program.
Environmental Education Centers (Ceam)
(GRI EN12)
Ceam Barreiro
Situated in an area of special protection for environmental preservation (State Decree No. 22,091, of June 8, 1982), has 880 acres, Where is also located a source responsible for strengthening the supply for the local population.
The structure of the CEAM Barreiro enables the community to use as a source of information and awareness about the importance of environmental preservation, especially for the guaranteed sources of supply. Environmental initiatives developed awareness of visitors seeking to preserve the area through participation in environmental workshops and fun activities with the use of an interpretive trail that runs along part of the river bed and part of the forest that surrounds the area.
In 2013, about 3,700 people, including students and teachers from 78 educational institutions, businesses, employees and other representatives of the company visited the center. Other environmental education initiatives have also been developed directly in schools (seminars, lectures, other activities), focused on the theme of sanitation to approximately 1,430 students.
Ceam Curvelo
In 2012, we implemented the CEAM in Curvelo, in partnership with the Federal Center of Technological Education of Minas Gerais. Located in the area of water treatment station of the city, the space is used for development of environmental education for the entire community.
Ceam ETE Arrudas e ETE Betim
The Arrudas ETE has a CEAM created with the objective of carrying out activities related to the environment and promote awareness of environmental preservation. Among other activities, it is a place of visitation open to the public. The CEAM Arrudas ETE is to highlight the biomonitoring system, consisting of an aquarium of about ten thousand liters, which is powered exclusively by liquid resulting from sewage treatment ETE, allowing you to control the quality of the final effluent of the treatment plant before to be released in Ribeirão Arrudas. One of the peculiarities of that biomonitoring is the use of fish in the São Francisco basin itself as an indicator of efficiency. Among the various species found there: matrinxã, mandi-yellow, curimatã piau and white. The CEAM ETE Betim been in operation since November 2013 and is similar to the ETE Arrudas.
Education water consumption
Copasa Minister lectures in industries, schools, hospitals, condominiums, public bodies and businesses, addressing issues related to the overall performance of the Company in relation to water supply, sewage collection and treatment systems and environmental education supplies. Information aimed at raising public awareness of the need for environmental preservation and combating waste water, as well as tips for leak detection and cleaning of water tank are presented. In 2013, 163 lectures were held, given an approximate audience of 12,290 people, while 63% were taught in educational institutions.
Monitored visits
Aiming to educate the community about the importance of conservation of water sources and rational use of water resources, by demonstrating the various stages of the production process, such as collection, treatment and distribution of water, Copasa keeps monitored visits in their systems basic sanitation services.
Integrated environmental action
Through playful actions, lectures and public hearings, the Company holds meetings which aim to engage participants on issues related to environmental education. In 2013, we highlight the achievement of educational games, contests phrases, drawings and essays relating to sanitation, benefiting more than two thousand people.
